
再次證實PRP的抗纖維化作用
再次證實PRP的抗纖維化作用
研究檢測 PRP 對乙型轉化生長因子 (TGF)-β1 所誘導的纖維母細胞(fibroblasts)分化為肌纖維母細胞(Myofibroblast)的影響(這是纖維化的主要因素)並研究使用 PRP對於的血管內皮生長因子 (VEGF)-A 的作用也評估單獨使用 PRP 對於纖維母細胞分化的影響。結果顯示出PRP 會通過 VEGF-A/VEGF 受體 (VEGFR)-1 所媒介的 TGF-beta1/Smad3 訊息傳遞路徑抑制負調節纖維母細胞-肌纖維母細胞的轉化也會消除 TGF-β1 所誘導的 VEGF-A 和 VEGFR-1 表達量減少。
PRP科技新知- 再次證實PRP的抗纖維化作用
研究背景:
研究PRP的抗纖維化效果。檢測 PRP 對乙型轉化生長因子 (TGF)-β1 所誘導的纖維母細胞(fibroblasts)分化為肌纖維母細胞(Myofibroblast)的影響(這是纖維化的主要因素);並研究使用 PRP對於的血管內皮生長因子 (VEGF)-A 的作用;也評估單獨使用 PRP 對於纖維母細胞分化的影響。
研究方法:
使用以下方法來評估肌纖維母細胞的細胞表型: 共聚焦螢光顯微鏡、使用西方墨點法來鑑定α-平滑肌肌動蛋白 (alpha-smooth muscle actin, sma) 和 第1型膠原蛋白(type-1 collagen)的表現量、富含黏着斑蛋白的局部沾黏(vinculin-rich focal adhesion clustering)、應力纖維組件(stress fiber assembly)。使用 RT-PCR 分析 Notch-1、連接蛋白 43 (connexin 43) 和 VEGF-A 的表達。
結果:
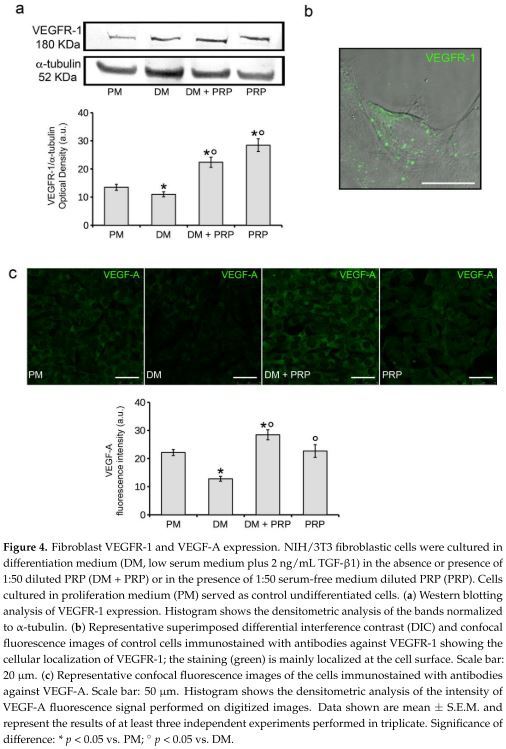
PRP 會通過 VEGF-A/VEGF 受體 (VEGFR)-1 所媒介的 TGF-beta1/Smad3 訊息傳遞路徑抑制負調節纖維母細胞-肌纖維母細胞的轉化。共同使用TGF-β1/PRP 的纖維母細胞顯示出肌纖維母細胞表型的強烈衰減,同時 Smad3 表達量降低。 抑制VEGFR-1 (如使用KRN633,這是一種血管內皮生長的抑制劑)會減少 PRP 的效果。此外,PRP 會消除 TGF-β1 所誘導的 VEGF-A 和 VEGFR-1 表達量減少。
結論: 使用 VEGF-A 進行細胞研究可證實 VEGF-A 信號傳導在對抗肌纖維母細胞生成中的作用。 PRP 作為單一治療不會誘導纖維母細胞肌分化。這項研究對於 PRP 的抗纖維化作用的細胞和分子機制提供了新的見解。
原文摘要:
The antifibrotic potential of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is controversial. This study examined the effects of PRP on in vitro transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, the main drivers of fibrosis, and the involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A in mediating PRP-induced responses. The impact of PRP alone on fibroblast differentiation was also assessed. Myofibroblastic phenotype was evaluated by confocal fluorescence microscopy and western blotting analyses of alpha-smooth muscle actin (sma) and type-1 collagen expression, vinculin-rich focal adhesion clustering, and stress fiber assembly. Notch-1, connexin 43, and VEGF-A expression were also analyzed by RT-PCR. PRP negatively regulated fibroblast-myofibroblast transition via VEGF-A/VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-1-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. Indeed TGF-beta1/PRP co-treated fibroblasts showed a robust attenuation of the myofibroblastic phenotype concomitant with a decrease of Smad3 expression levels. The VEGFR-1 inhibition by KRN633 or blocking antibodies, or VEGF-A neutralization in these cells prevented the PRP-promoted effects. Moreover PRP abrogated the TGF-beta1-induced reduction of VEGF-A and VEGFR-1 cell expression. The role of VEGF-A signaling in counteracting myofibroblast generation was confirmed by cell treatment with soluble VEGF-A. PRP as single treatment did not induce fibroblast myodifferentiation. This study provides new insights into cellular and molecular mechanisms underpinning PRP antifibrotic action.
文章出處:
Chellini F, Tani A, Vallone L, Nosi D, Pavan P, Bambi F, Zecchi Orlandini S, Sassoli C: Platelet-Rich Plasma Prevents In Vitro Transforming Growth Factor-beta1-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition: Involvement of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-A/VEGF Receptor-1-Mediated Signaling (dagger). Cells 2018, 7(9).
研究背景:
研究PRP的抗纖維化效果。檢測 PRP 對乙型轉化生長因子 (TGF)-β1 所誘導的纖維母細胞(fibroblasts)分化為肌纖維母細胞(Myofibroblast)的影響(這是纖維化的主要因素);並研究使用 PRP對於的血管內皮生長因子 (VEGF)-A 的作用;也評估單獨使用 PRP 對於纖維母細胞分化的影響。
研究方法:
使用以下方法來評估肌纖維母細胞的細胞表型: 共聚焦螢光顯微鏡、使用西方墨點法來鑑定α-平滑肌肌動蛋白 (alpha-smooth muscle actin, sma) 和 第1型膠原蛋白(type-1 collagen)的表現量、富含黏着斑蛋白的局部沾黏(vinculin-rich focal adhesion clustering)、應力纖維組件(stress fiber assembly)。使用 RT-PCR 分析 Notch-1、連接蛋白 43 (connexin 43) 和 VEGF-A 的表達。
結果:
PRP 會通過 VEGF-A/VEGF 受體 (VEGFR)-1 所媒介的 TGF-beta1/Smad3 訊息傳遞路徑抑制負調節纖維母細胞-肌纖維母細胞的轉化。共同使用TGF-β1/PRP 的纖維母細胞顯示出肌纖維母細胞表型的強烈衰減,同時 Smad3 表達量降低。 抑制VEGFR-1 (如使用KRN633,這是一種血管內皮生長的抑制劑)會減少 PRP 的效果。此外,PRP 會消除 TGF-β1 所誘導的 VEGF-A 和 VEGFR-1 表達量減少。
結論: 使用 VEGF-A 進行細胞研究可證實 VEGF-A 信號傳導在對抗肌纖維母細胞生成中的作用。 PRP 作為單一治療不會誘導纖維母細胞肌分化。這項研究對於 PRP 的抗纖維化作用的細胞和分子機制提供了新的見解。
原文摘要:
The antifibrotic potential of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is controversial. This study examined the effects of PRP on in vitro transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, the main drivers of fibrosis, and the involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A in mediating PRP-induced responses. The impact of PRP alone on fibroblast differentiation was also assessed. Myofibroblastic phenotype was evaluated by confocal fluorescence microscopy and western blotting analyses of alpha-smooth muscle actin (sma) and type-1 collagen expression, vinculin-rich focal adhesion clustering, and stress fiber assembly. Notch-1, connexin 43, and VEGF-A expression were also analyzed by RT-PCR. PRP negatively regulated fibroblast-myofibroblast transition via VEGF-A/VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-1-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. Indeed TGF-beta1/PRP co-treated fibroblasts showed a robust attenuation of the myofibroblastic phenotype concomitant with a decrease of Smad3 expression levels. The VEGFR-1 inhibition by KRN633 or blocking antibodies, or VEGF-A neutralization in these cells prevented the PRP-promoted effects. Moreover PRP abrogated the TGF-beta1-induced reduction of VEGF-A and VEGFR-1 cell expression. The role of VEGF-A signaling in counteracting myofibroblast generation was confirmed by cell treatment with soluble VEGF-A. PRP as single treatment did not induce fibroblast myodifferentiation. This study provides new insights into cellular and molecular mechanisms underpinning PRP antifibrotic action.
文章出處:
Chellini F, Tani A, Vallone L, Nosi D, Pavan P, Bambi F, Zecchi Orlandini S, Sassoli C: Platelet-Rich Plasma Prevents In Vitro Transforming Growth Factor-beta1-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition: Involvement of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-A/VEGF Receptor-1-Mediated Signaling (dagger). Cells 2018, 7(9).

